
Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
Born on December 18, 1856 in Cheetham Hill, Manchester, United Kingdom – died on August 30, 1940 in Cambridge, United Kingdom.

Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
First female professor at a University in Paris, Sorbonne.

Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
Dedicated their time to discovering what made the mineral, pitchblend, radioactive.

Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card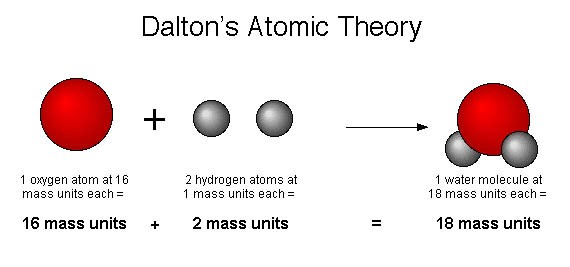
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
-All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible.
– All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties
-Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms.
-chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms.

Guess the Genius
Clue Card #17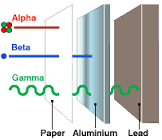
10 POINTS
Elaine, Nica, Christine and Natalia
-The first person to split the atom and considered to be the “Father of nuclear physics”
-He also identified radiations like alpha, beta and gamma rays

Guess the Genius
Clue Card #11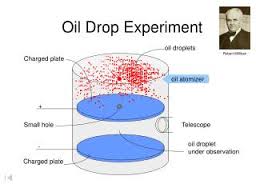
10 POINTS
Elaine, Nica, Christine and Natalia
-Born-died: March 22, 1868- December 19, 1953
-Won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 (his study of the elementary electronic charge and the photoelectric effect)
-Famous for his “Oil-drop experiment”

Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
Founded the Radium Institute to carry out medical research.

Do You Know Your Scientist?
Fact Card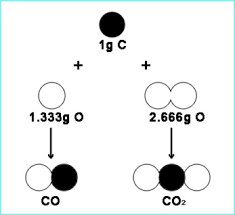
Catherine, Emma, Mabel, Rachel POINTS
Developed law of multiple proportions.

Guess the Genius
Clue Card #8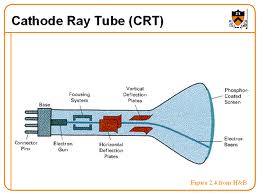
10 POINTS
Elaine, Nica, Christine, and Natalia
-Discovered the electron in 1897 as well as isotopes.
-Won the Nobel Prize in physics (1906) and was famous for using the cathode ray tube in his experiment.