Bacillariophyceae

Phytoplankton
Diatom Order


Sorry, there is no photo available. If you have one, please submit
here
.
2 POINTS
Fact: Diatoms belong to a large group called the heterokonts, including both autotrophs and heterotrophs
cold, cool, warm
Graphic by Ernst Haeckel (1904)
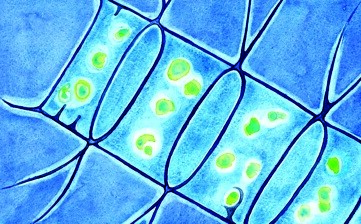
Diatoms[5] are a major group of algae, and are among the most common types ofphytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons (e.g. Fragilaria), fans (e.g. Meridion), zigzags (e.g. Tabellaria), or stars (e.g. Asterionella). Diatoms are producers within the food chain. A unique feature of […] read more

Diatom
Chaetocerus spp.

Sorry, there is no photo available. If you have one, please submit
here
.
3 POINTS
• Prochlorococcus spp. is a PLANKTON SPECIES.
cool, warm
Graphic by Melissa Guionwww.melissaguion.com
Chaetoceros is probably the largest genus of marine planktonic diatoms with approximately 400 species described. Although a large number of these descriptions are no longer valid. It is often very difficult to distinguish between different Chaetocerosspecies.[1] Several attempts have been made to restructure this large genus into subgenera and this work is still in progress[2][3]However, most of […] read more

Phytoplankton
Class: Bacillariophyceae


Sorry, there is no photo available. If you have one, please submit
here
.
1 POINT
Play: Symbiodinium spp has a MOVE of 1, and is often eaten by KRILL SPECIES.
Fact: Symbiodinium spp are also crucially dependent on minerals
cold, cool, warm
Graphic by Kyu Hwangkyuhwang.com/
Phytoplankton (English pronunciation: /ˌfaɪtoʊˈplæŋktən/) are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν (phyton), meaning “plant“, and πλαγκτός (planktos), meaning “wanderer” or “drifter”.[1] Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye. However, when present in high enough numbers, they may appear as a […] read more