Chordata

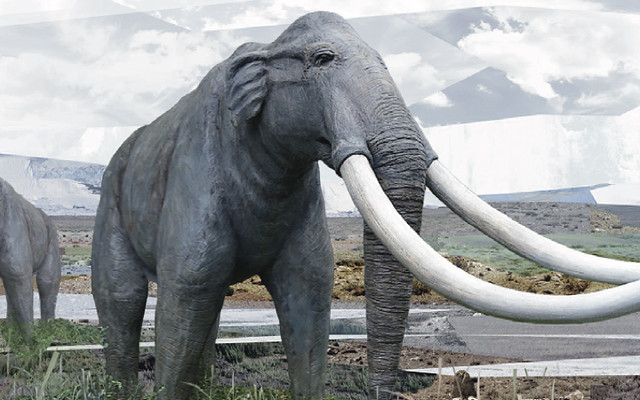
Straight-Tusked Elephant
Palaeoloxodon antiquus


EXTINCT | 5 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 1
FACT: The straight-tusked elephant is closely related to the existing African forest elephant. It had up to three meters long tusks. It spread from Central and Southern Europe to the north in the warmer periods.

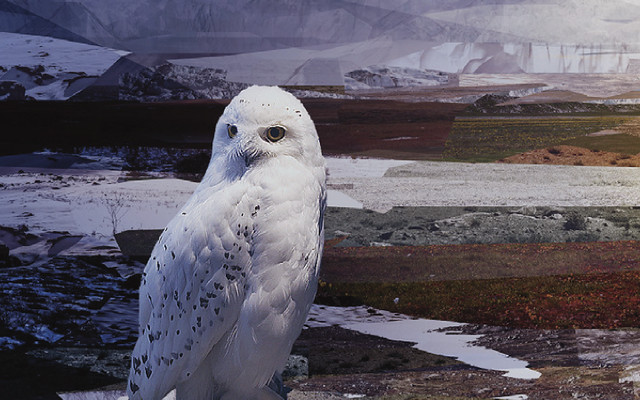
Snowy Owl
Bubo scandiacus


6 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 3. Diagonally in an arctic climate.
FACT: The snowy owl does not breed if the lemming population is very small. Contrary, it hatches multiple chicks when the lemming population is great.

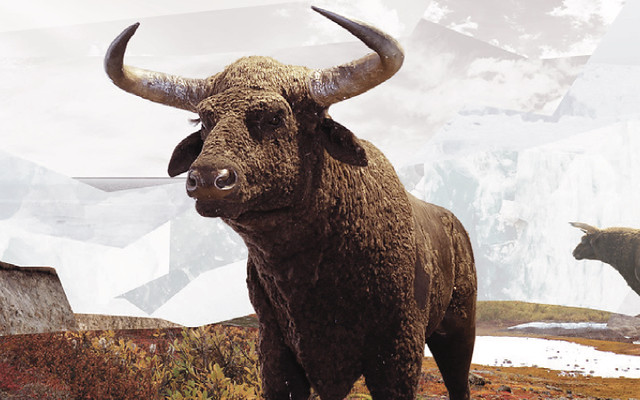
Aurochs
Bos primigenius


EXTINCT | 5 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 1
FACT: The aurochs are the ancestor of domestic cattle. The aurochs were an important but dangerous prey species for the hunters of the Mesolithic period. The 80 cm long and forward-curving horns of the bulls and their large body made them a dangerous opponent.

Irish Elk
Megaloceros giganteus latidens


EXTINCT | 6 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 1
FACT: The antlers of the Irish elk are the largest antlers of all known species of deer. It had a span up to four meters and weighed up to 40 kg. In order to grow 40 kg heavy antlers every year; a lot of calcium rich food is required.

Cave Bear
Ursus spelaeus


EXTINCT | 5 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 1
FACT: As an adaptation to the cold, the cave bear grew during the Ice Age, as a larger body insulates better against the cold. Teeth of cave bears were typically more worn down than teeth of today’s brown bears. This suggest that they were more herbivorous than today’s brown bears.

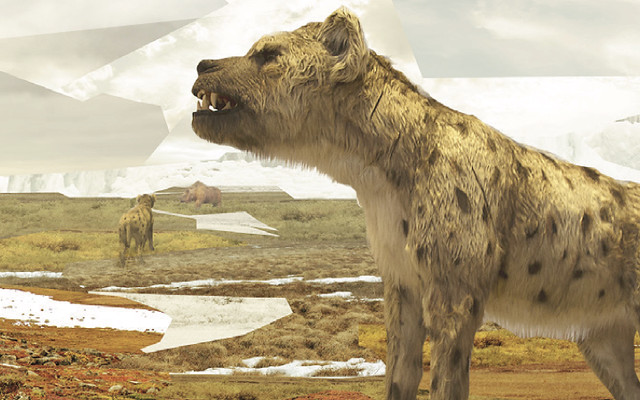
Cave Hyena
Crocuta crocuta spelaea


EXTINCT | 9 POINTS
PLAY: Move of 2. The card can even feed on herbivores of scale 9. If the Cave hyena is next to another Cave hyena, add one extra point.
FACT: Hyenas are more closely related to cats than dogs. By means of the powerful jaws and teeth of the cave hyena it could crush very dense bones.