United Kingdom Vintage Deck
2014 – (See Cards | Deck Info | Download | Purchase)…
All organisms collected depict common flora and fauna found in the United Kingdom. This is a DIY 60 card STARTER deck that collects vintage biodiversity related illustrations that predate 1913 (at least one hundred years old). Most come from wiki commons or the Biodiversity Heritage Library, where copyright status appears clear. Note that if an image used are breaking copyright status, please contact db@mail.ubc.ca so that we can remove the image.

Common Frog
Rana temporaria


8 POINTS
Play: Common Frog has a MOVE of 2.
Fact: In some places, this frog may be trapped under ice for up to 9 months, but studies have shown that they may still be relatively active at temperatures close to freezing.

Common Octopus
Octopus vulgaris


8 POINTS
Play: The Common Octopus has a MOVE of 2.
Fact: The Common Octopus is able to colour blend with its surroundings.

Sperm Whale
Physeter macrocephalus


8 POINTS
Play: The Sperm Whale has a MOVE of 2.
Fact: From the early 18th century through the late 20th, the species was a prime target of whalers. The head of the whale contains a liquid wax known as spermaceti, from which the whale derives its name.

Mute Swan
Cygnus olor

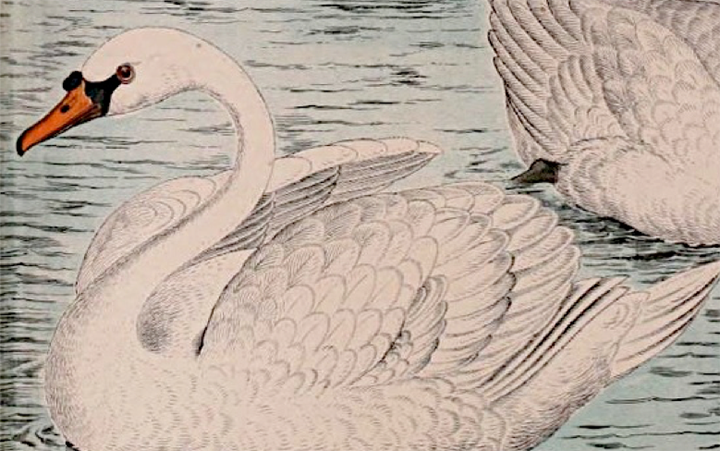
4 POINTS
Play: The Mute Swan has a FLIGHT of 2.
Fact: The Mute Swan is one of the heaviest flying birds, with males (known as cobs) averaging about 24 to 26lbs.

Green Woodpecker
Picus viridis


7 POINTS
Play: The Green Woodpecker has a FLIGHT of 2.
Fact: Like other woodpeckers, the Green Woodpecker’s tongue is long (10cm) and has to be curled around its skull.

Human
Homo sapiens


3 POINTS
Play: This Human has a MOVE of 2. Can be played next to any TERRAIN.
Fact: Although an omnivore, this card can only be played next to a SPECIES card that represents food that the player would actually eat.