Microbe Collection
Ongoing – (See Cards)…
This set simply aims to collect “microorganisms” as loosely as defined as those species that are multicellular, singled cell or smaller (essentially SCALE value of 3 or less). Given the incredible diversity and abundance of species in this category, the Phylo project is hopeful that this collection will grow to represent this important part of biodiversity.

Copepoda
Subclass


2 POINTS
Play: Copepoda have a MOVE of 2.
Fact: Copepods are major ZOOPLANKTON

Cyanobacteria
Prochlorococcus spp.



2 POINTS
Play: Prochlorococcus is a PLANKTON SPECIES.
Fact: This is possibly the Earth’s most plentiful species & accounts for an estimated 20% of the oxygen in the atmosphere.

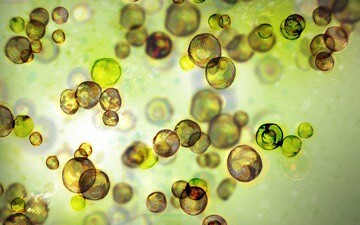
Zooxanthellae
Symbiodinium spp.

3 POINTS
• ZOOXANTHELLAE is a PLANKTON SPECIES.
• ZOOXANTHELLAE must be present to play WARM WATER CORAL SPECIES (SYMBIOTIC relationship).

Diatom
Chaetocerus spp.

3 POINTS
• Prochlorococcus spp. is a PLANKTON SPECIES.

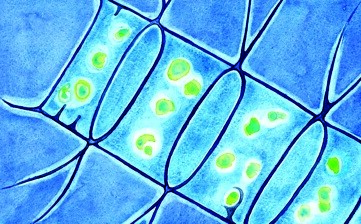
Cyanobacteria
Tolypothrix spp.


2 POINTS
Play: Tolypothrix spp. is a PLANKTON SPECIES.

Sea Sparkle
Noctiluca scintillans



5 POINTS
Play: The bioluminescence Noctiluca scintillans is a PLANKTON that feeds off of other PLANKTON SPECIES.
Play: It must be played adjacent to at least 1 compatible PLANKTON SPECIES.