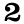Diatoms[5] are a major group of algae, and are among the most common types ofphytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons (e.g. Fragilaria), fans (e.g. Meridion), zigzags (e.g. Tabellaria), or stars (e.g. Asterionella). Diatoms are producers within the food chain. A unique feature of diatom cells is that they are enclosed within a cell wall made of silica (hydrated silicon dioxide) called a frustule. These frustules show a wide diversity in form, but are usually almost bilaterally symmetrical, hence the group name. The symmetry is not perfect since one of the valves is slightly larger than the other allowing one valve to fit inside the edge of the other. Fossilevidence suggests that they originated during, or before, the early Jurassic Period. Only male gametes of centric diatoms are capable of movement by means of flagella. Diatom communities are a popular tool for monitoring environmental conditions, past and present, and are commonly used in studies of water quality.
(From Wikipedia, March 2015)