Ephedrine (![]() i/ɨˈfɛdrɪn/ or /ˈɛfɨdriːn/; not to be confused with ephedrone) is a sympathomimeticamine and substituted amphetamine commonly used as a stimulant, concentration aid,decongestant, appetite suppressant, and to treat hypotension associated with anaesthesia.
i/ɨˈfɛdrɪn/ or /ˈɛfɨdriːn/; not to be confused with ephedrone) is a sympathomimeticamine and substituted amphetamine commonly used as a stimulant, concentration aid,decongestant, appetite suppressant, and to treat hypotension associated with anaesthesia.
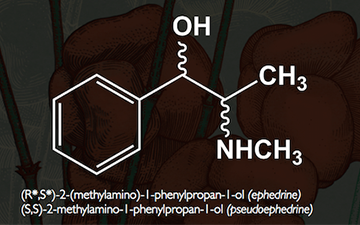
Ephedrine is similar in molecular structure to the well-known drugs phenylpropanolamine andmethamphetamine, as well as to the important neurotransmitter epinephrine (adrenaline). Chemically, it is an alkaloid with a phenethylamine skeleton found in various plants in the genusEphedra (family Ephedraceae). It works mainly by increasing the activity of norepinephrine(noradrenaline) on adrenergic receptors.[1] It is most usually marketed as the hydrochloride or sulfate salt.
The herb Ephedra sinica, used in traditional Chinese medicine, contains ephedrine andpseudoephedrine as its principal active constituents. The same may be true of other herbal products containing extracts from other Ephedra species.