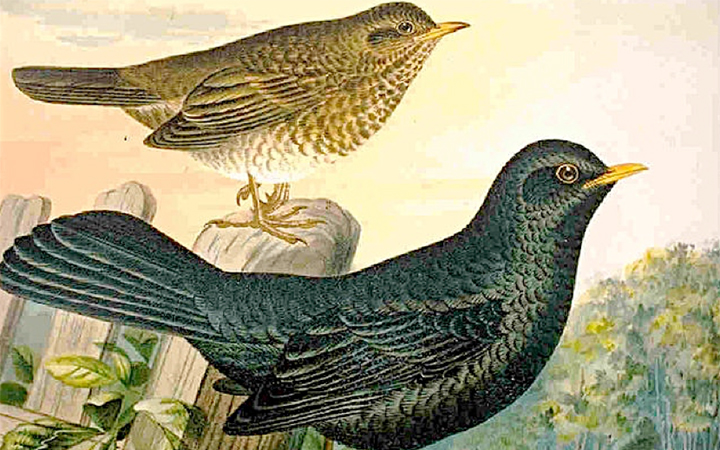
The common blackbird (Turdus merula) is a species of true thrush. It is also called Eurasian blackbird (especially in North America, to distinguish it from the unrelatedNew World blackbirds),[2] or simply blackbird where this does not lead to confusion with a similar-looking local species. It breeds in Europe, Asia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to Australia (where it is considered a pest) and New Zealand. It has a number of subspecies across its large range; a few of the Asian subspecies are sometimes considered to be full species. Depending on latitude, the common blackbird may be resident, partially migratory or fully migratory.
The male of the nominate subspecies, which is found throughout most of Europe, is all black except for a yellow eye-ring and bill and has a rich melodious song; the adult female and juvenile have mainly dark brown plumage. This species breeds in woods and gardens, building a neat, mud-lined, cup-shaped nest. It is omnivorous, eating a wide range of insects, earthworms, berries, and fruits.
Both sexes are territorial on the breeding grounds, with distinctive threat displays, but are more gregarious during migration and in wintering areas. Pairs will stay in their territory throughout the year where the climate is sufficiently temperate. This common and conspicuous species has given rise to a number of literary and cultural references, frequently related to its song.
(From Wikipedia, March 2015)