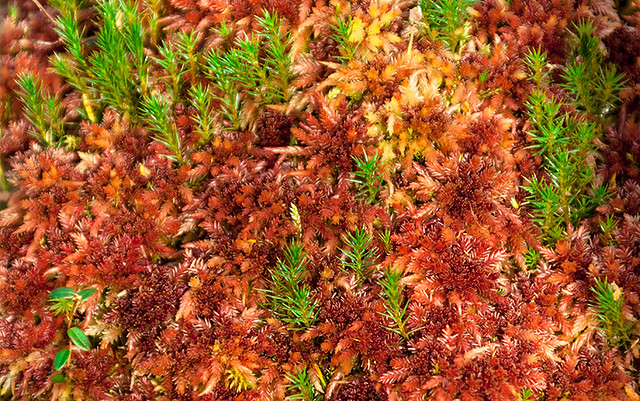
Sphagnum is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species[2] of mosses, commonly known as peat moss. Accumulations of Sphagnum can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16–26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.[3] The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. Hence, as sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs.[4] These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plants.[5] Sphagnum and the peat formed from it do not decay readily because of the phenolic compounds embedded in the moss’s cell walls. In addition, bogs, like all wetlands, develop anaerobic soil conditions, which produces slower anaerobic decay rather than aerobic microbial action. Peat moss can also acidify its surroundings by taking up cations, such as calcium and magnesium, and releasing hydrogen ions. Under the right conditions, peat can accumulate to a depth of many meters. Different species of Sphagnum have different tolerance limits for flooding and pH, so any one peatland may have a number of different Sphagnum species.[6]
Individual peat moss plants consist of a main stem, with tightly arranged clusters of branch fascicles usually consisting of two or three spreading branches and two to four hanging branches. The top of the plant, or capitulum, has compact clusters of young branches. Along the stem are scattered leaves of various shapes, named stem leaves; the shape varies according to species. The leaves consist of two kinds of cells; small, green, living cells (chlorophyllose cells), and large, clear, structural, dead cells (hyaline cells). The latter have the large water-holding capacity.
(From: Wikipedia, April 2017)