Cards
(QUICK LINKS: Decks | plants | mammals | birds | | reptiles | fish | cephalopoda | insects | microbe | events
( scientist | project | modifier | technique |)

Satureja darwinii
Clinopodium darwinii


2 POINTS
Fact: Darwin writes: “Very sweet smelling, plant; with a rather biting aromatic taste; used for making tea by the seamen.”

Floreana Mockingbird
Mimus trifasciatus


3 POINTS
Play: The Floreana Mockingbird has a FLIGHT of 2.
Fact: The Floreana Mockingbird is critically endangered and is on the brink of extinction.

Geonoma schottiana
Arecaceae geonoma schottiana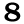


2 POINTS
FACT: Specimens of this plant were collected by Darwin at Bahia (Salvador) in March 1832.

Galapagos sea lion
Zalophus wollebaeki



8 POINTS
Play: This sea lion has a MOVE of 2.
Fact: Their loud bark, playful nature, and graceful agility in water make them the “welcoming party” of the Galapagos Islands.

Aeronaut Spider
Parasteatoda tepidariorum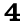


6 POINTS
Play: These spiders have a FLIGHT of 2.
“How inexplicable is the cause which induces these small insects, as it now appears in both hemispheres, to undertake their aerial excursions.” ~Darwin (Oct 31, 1832)

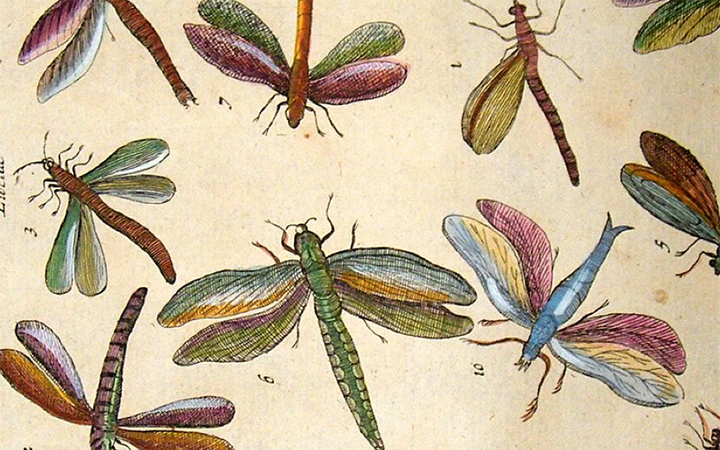
Dragonfly
Anisoptera Infraorder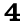


7 POINTS
Play: The Dragonfly has a FLIGHT of 2.
Fact: In general, large dragonflies have a maximum speed of 10 to 15 metres per second (22 to 34 mph.)